Top 10 Design Trends for Custom Glass in Modern Interiors
Top 10 Design Trends for Custom Glass in Modern Interiors (2025)
Updated · Trends & Design by Glass Helper
Glass is no longer just a window to the outside — in 2025 it’s a bold design element.
Here are the top 10 trends shaping custom glass use in modern interiors, from soft curves to smart innovations.
1) Curved & Organic Glass Forms
Curved partitions and glass furniture pieces are softening the hard edges of modern spaces.
According to Saint-Gobain,
rounded edges and organic shapes will dominate in 2025 for a more fluid architectural aesthetic.
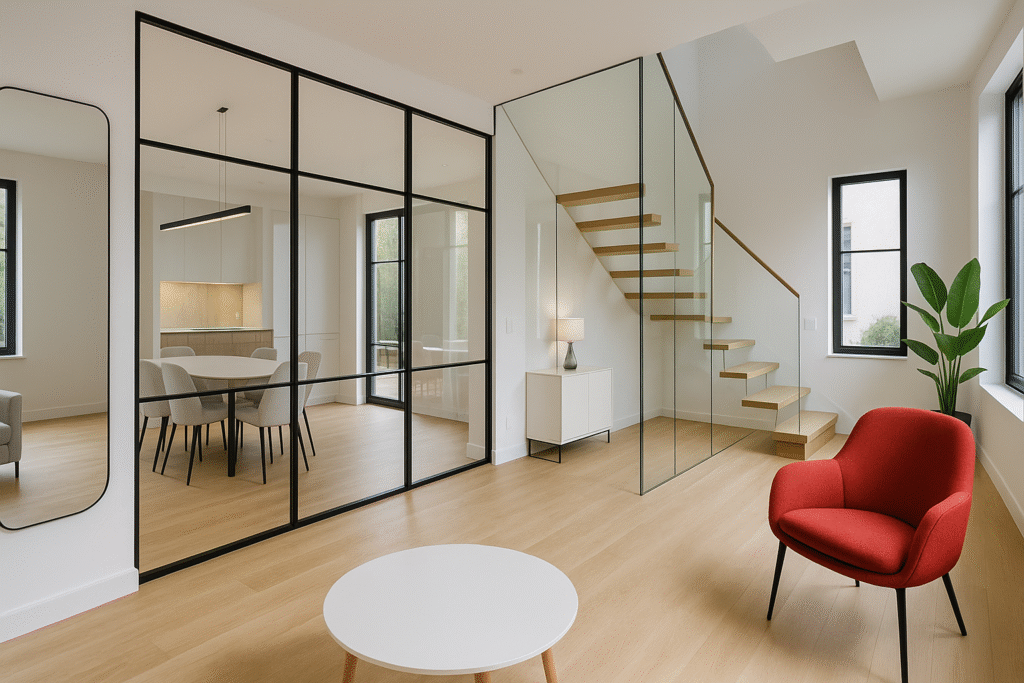
2) Floor-to-Ceiling & Oversized Panels
Large glass panels create open, airy spaces and enhance light flow.
Guardian Glass reports that
new coatings and structural systems allow wider panes without heat loss or distortion.
3) Textured, Reeded & Ribbed Surfaces
Designers are rediscovering the beauty of tactile finishes.
KP Glass
calls reeded glass a retro comeback, while
Architectural Glass
highlights how patterns enhance privacy and style simultaneously.
4) Digitally Printed & Decorative Glass
High-definition printing and etching allow custom artwork, patterns, and branding directly on glass.
ToughGlaze
lists digital printing as one of the top ways to make glass both functional and expressive.
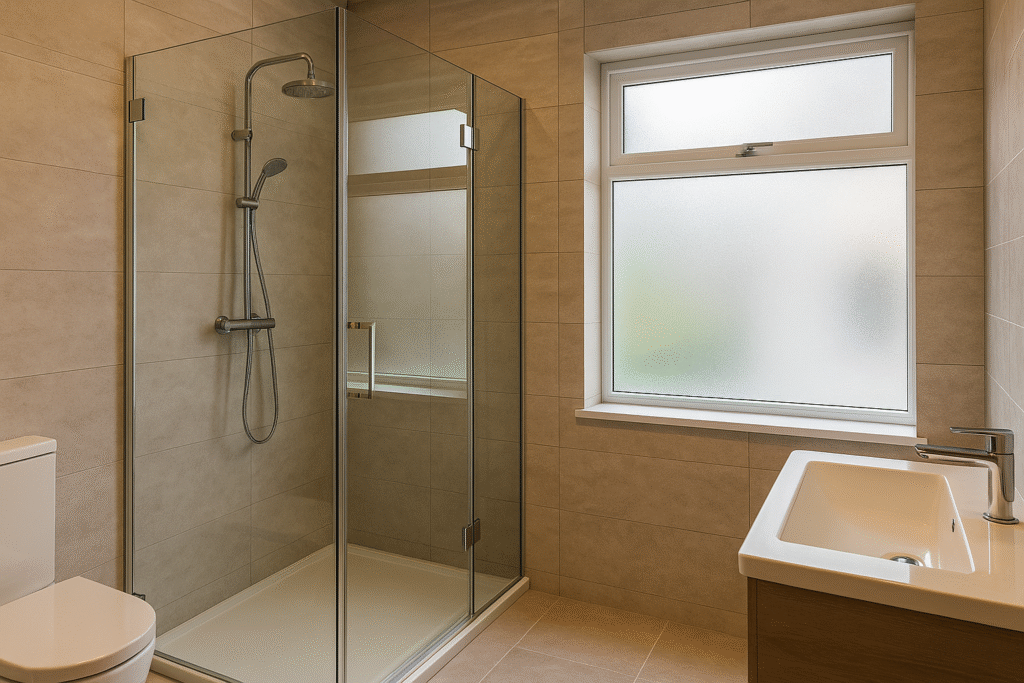
5) Smart / Switchable Glass
Switchable (PDLC or electrochromic) glass lets you control privacy with a button — a growing trend in luxury interiors.
Hallmark Glass
highlights its use in bathrooms, offices, and smart homes.
6) Colored & Tinted Glass Layers
From subtle greys to bold bronzes, colored interlayers are adding mood and warmth.
Both ToughGlaze
and Saint-Gobain Glass UK
predict colored glass will feature in balustrades, partitions, and furniture in 2025.
7) Minimal Frameless & Floating Systems
Thin profiles and invisible fixings keep designs sleek.
KP Glass
and Architectural Glass
both identify frameless glazing as a staple of minimal interiors.
8) Internal Glazing & Partition Walls
Internal glass walls define zones while preserving natural light.
Cantifix
explores how glass partitions reshape homes and offices, combining openness with acoustic control.
9) Sustainable & High-Performance Glass
Energy-efficient glazing and low-iron clarity are essential in eco-friendly interiors.
Guardian Glass
notes that 2025 designs must merge sustainability with aesthetics to meet environmental targets.
10) Revival of Stained & Artistic Glass
Stained and engraved glass art is making a stylish comeback.
House & Garden
showcases how modern homes now feature artistic panels that balance tradition with contemporary design.
Explore Custom Glass Options
Tailor-made glass for partitions, balustrades, splashbacks & more — delivered UK-wide.
Sources & Further Reading
- Saint-Gobain Glass India – 2025 Trends
- Guardian Glass – Design with Glass: 6 Trends
- KP Glass Glazing – Trends in Glass Installation
- Architectural Glass – Decorative Trends
- ToughGlaze – Interior Design Trends
- Cantifix – Internal Glazing Insight
- House & Garden – Stained Glass Revival
- Hallmark Glass – Modern Glass Trends 2025